234 Productos
Tornillos, tuercas, pernos, arandelas y elementos de fijación no magnéticos
Why are non-magnetic fasteners needed?
Non-magnetic polymer fasteners are needed in applications where the presence of magnetic materials could interfere with sensitive equipment or processes. In industries like medical imaging (such as MRI machines), aerospace, and electronics, non-magnetic fasteners prevent magnetic fields from disrupting the operation of critical devices. They are also essential in military and defense applications, where magnetic signatures must be minimized for stealth purposes. Additionally, non-magnetic fasteners are used in scientific instruments, data storage, and telecommunications equipment to ensure accurate measurements and reliable performance, as magnetic interference can cause data corruption or operational failures.

Non-Magnetic Fastener Materials
There are a variety of non-magnetic polymers that can be used to make screws, nuts, bolts, washers, and fasteners due to their low magnetic susceptibility, which makes them suitable for use in applications where magnetic fields are a concern.
All fasteners provided by HPP are non-magnetic complaint, however, below outlines our key non-magnetic polymer fastener materials:
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): PEEK is a type of polymer that is made from monomers called ketones. It is a non-magnetic material that is known for its excellent mechanical and thermal properties, as well as its chemical resistance and good electrical insulation properties.
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS): PPS is a type of polymer that is made from monomers called phenylenes and sulfides. It is a non-magnetic material that is known for its excellent thermal stability and high temperature resistance, as well as its good chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): PTFE is a type of polymer that is made from monomers called tetrafluoroethylenes. It is a non-magnetic material that is known for its excellent chemical resistance, low coefficient of friction, and high temperature resistance.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): PVC is a type of polymer that is made from monomers called vinyl chlorides. It is a non-magnetic material that is known for its good chemical resistance, low cost, and versatility.
Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate is a type of polymer that is made from monomers called carbonates. It is a non-magnetic material that is known for its excellent mechanical properties, high temperature resistance, and good electrical insulation properties.
Non-Magnetic Fastener Applications
Non-magnetic polymer screws, nuts, bolts, washers, and fasteners may be used in a variety of applications where magnetic fields are a concern, such as in the construction of medical equipment or in the assembly of electronic components. They may also be used in the manufacture of non-magnetic materials or in the installation of electrical systems.
In addition to their use in the medical, military, and aerospace industries, non-magnetic polymer fasteners may also be used in other applications where magnetic fields are a concern, such as in the construction of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines or in the operation of military equipment. They may also be used in environments where magnetic materials are not desired, such as in the assembly of scientific instruments or in the transportation of sensitive materials.

What makes these polymers non-magnetic?
Polymer fasteners are non-magnetic because they are made from organic compounds that lack the free electrons and metallic elements required to generate a magnetic field. Unlike metals, which contain atoms with unpaired electrons that can align and create magnetism, polymers are composed of long chains of non-metallic elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. These elements do not interact with magnetic fields, making the material inherently non-magnetic. Additionally, the manufacturing process avoids the use of metallic additives or fillers that could introduce magnetic properties, ensuring that the fasteners remain non-magnetic. This makes polymer fasteners ideal for applications where magnetic interference must be avoided.

What are the benefits of non-magnetic fasteners?
Non-magnetic polymer fasteners offer several benefits, including the elimination of magnetic interference, making them ideal for sensitive equipment like MRI machines, aerospace systems, and scientific instruments. They are corrosion-resistant, durable in harsh environments, and lightweight, which is beneficial for reducing system weight in industries like aerospace and automotive. Additionally, these fasteners provide electrical insulation and resist chemicals, ensuring long-term performance in industrial, chemical, and outdoor applications. Their combination of non-magnetic properties, durability, and versatility makes them valuable in environments requiring both reliability and magnetic neutrality.
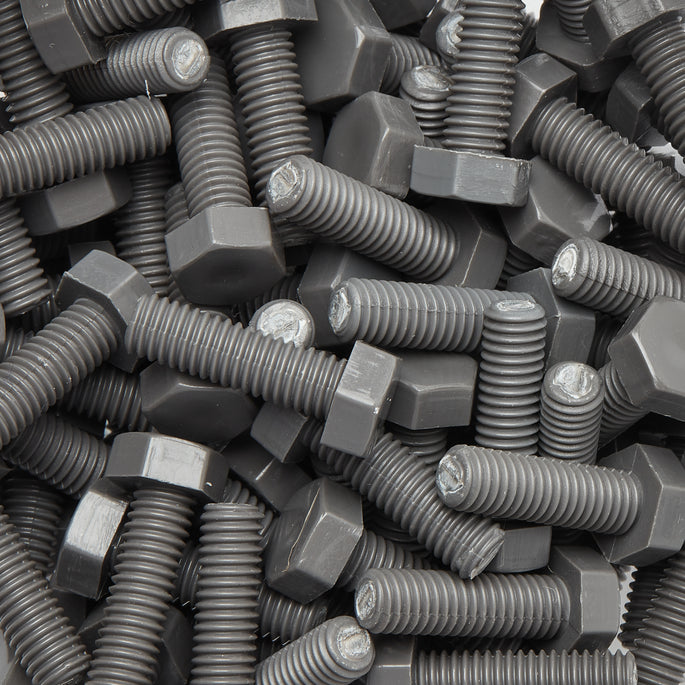

Other Benefits Of Non-Magnetic Fasteners
Other beneficial properties of non-magnetic fasteners include; corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. They can help to improve the safety and reliability of medical and electronic systems, and they can help to prevent interference from magnetic fields.
Los tornillos, tuercas, pernos, arandelas y elementos de fijación de polímeros no magnéticos están fabricados con polímeros de baja susceptibilidad magnética. Se utilizan en una variedad de aplicaciones en las que los campos magnéticos son un problema, como en las industrias médica, militar y aeroespacial, o en entornos en los que no se desean materiales magnéticos.
Existe una gran variedad de polímeros no magnéticos que pueden utilizarse para fabricar tornillos, tuercas, pernos, arandelas y elementos de fijación, como el polietileno, el polipropileno y el politetrafluoroetileno (PTFE). Estos polímeros son conocidos por su baja susceptibilidad magnética, lo que los hace adecuados para su uso en aplicaciones en las que los campos magnéticos son una preocupación.
Los tornillos, tuercas, pernos, arandelas y elementos de fijación de polímeros no magnéticos pueden utilizarse en diversas aplicaciones en las que los campos magnéticos son un problema, como en la construcción de equipos médicos o en el montaje de componentes electrónicos. También pueden utilizarse en la fabricación de materiales no magnéticos o en la instalación de sistemas eléctricos.
Los elementos de fijación de polímeros no magnéticos suelen elegirse por su baja susceptibilidad magnética, así como por sus otras propiedades beneficiosas, como la resistencia a la corrosión y sus buenas propiedades mecánicas. Pueden contribuir a mejorar la seguridad y fiabilidad de los sistemas médicos y electrónicos, así como a evitar las interferencias de los campos magnéticos.
Además de su uso en las industrias médica, militar y aeroespacial, los elementos de fijación de polímeros no magnéticos también pueden utilizarse en otras aplicaciones en las que los campos magnéticos son una preocupación, como en la construcción de máquinas de resonancia magnética (IRM) o en el funcionamiento de equipos militares. También pueden utilizarse en entornos en los que los materiales magnéticos no son deseables, como en el montaje de instrumentos científicos o en el transporte de materiales sensibles.